Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis (IBR; also known as infectious pustular vulvovaginitis, IPV), is a disease of cattle caused by infection with Bovine herpesvirus type 1.
IBR causes severe respiratory disease that can lead to fatal pneumonia. The virus can infect the upper respiratory tract and/or the reproductive tract. Mortality is low, but economic losses can be important. The severity of clinical signs depends on the strain of the virus and the susceptibility of cattle. In adult cows, infection is associated with a severe and prolonged drop in milk yield, reduced fertility and abortions, and inflammation of the vulva/prepuce.
The cost: £5–7m (Bennett R. 2005) to the national herd in health and productivity loss.
Seven vaccines for IBR were marketed in the UK:
- Bovilis IBR marker live contains modified live gE-negative Bovine herpesvirus type 1 (BHV-1)
- Bovilis IBR Marker Inac contains inactivated gE-negative BHV-1
- Hiprabovis IBR Marker Live contains live gE-tk- double gene-deleted BHV-1
- Rispoval IBR-Marker Inactivated contains inactivated gE-negative BHV-1
- Rispoval IBR-Marker Live contains live gE-negative BHV-1
- Tracherine contains live attenuated BHV-1
Assumptions
Numerator: The number of doses of vaccine administered has been calculated by multiplying the number of packs sold by the number of doses per pack.Denominator: It was assumed that cattle of all ages should be vaccinated and that the at-risk population was all cattle and calves in the UK.
All cattle are potentially at risk of IBR. Common industry practice would be for cattle to be vaccinated for the first time before the age of one year, with one dose of IBR vaccine. Approximately 40% of farmers who use IBR vaccines in cattle over one year of age give two boosters annually, but about 60% only give one IBR booster vaccine per year. To take this into account, the denominator was, therefore, the number of calves under one year plus the number of cattle over one year multiplied by 1.4.
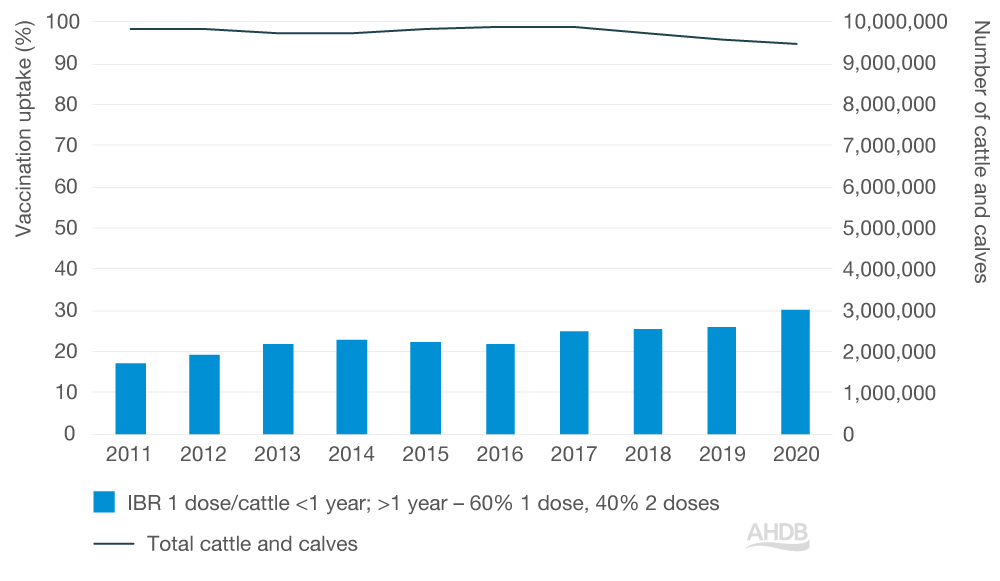
Vaccination uptake
IBR vaccine uptake steadily increased from 17% in 2011, to a high of 30% in 2020. Since 2017, it has been estimated that over one in four of all cattle in the UK are being vaccinated against IBR.